Eurite
Eurite: Name originally suggested by d'Aubuisson for a compact felsitic rock and later extended to cover all aphanitic rocks of granitic composition. From the Greek eurys = broad.
Elba island Eurite
The La Crocetta deposit is located in the Eastern portion of Elba island, which lies in the Northern Tyrrhenian Sea, between the Corsica Island and the Tuscan coast (
Fig.1). In his pioneering study of Elba, Trevisan (1950) recognized five major thrust complexes, numbered (I-V) from the bottom to the top in their structural position. The five complexes were assigned to either the Tuscan palaeodomain (complexes I, II, and III) and to the Ligurian oceanic realm (complexes IV and V). La Crocetta deposit is embedded in complex V, close to the contact with the underlying complex IV. Complex V, the uppermost structural unit, essentially consists of two members. The lower one, a Palaeocene-Eocene pelitic (argillites, calcarenites and sandy marls) succession, is interbedded with ophiolitic breccias, and is strongly tectonized. The upper member consists of Cretaceous flysch, basically made up of limestone beds, calcareous shales, and feldspathic sandstones. Complex IV, on the other hand, consists of Jurassic ophiolitic rocks and overlying Late Jurassic-Middle Cretaceous cherts, limestones and argillites.
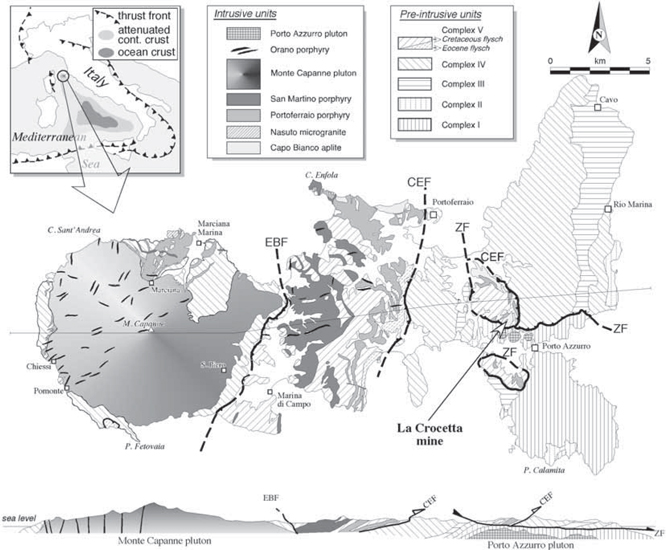
Fig.1: Geology of Elba Island. After Benvenuti, M (2006).
The La Crocetta mine is located in the Eastern part of Elba island, about 2.5 km North-West of the town of Porto Azzurro (
Fig.2). The local geology is characterized by the Capo Bianco porphyritic aplites and subordinated monzogranitic porphyries, which are emplaced as large sills and dikes that can vary in thickness from about 10 to 100 m. The intrusions occur within the lowermost part of complex V, at the contact between Cretaceous flysch and Palaeocene-Eocene pelite. The Capo Bianco eurites are located along this contact, and are cut by a small dike of monzogranitic porphyry.
Given their close spatial and temporal relationships with ore-forming systems, sericitic alteration and K-metasomatism of intrusive rocks have been extensively studied in many geological settings. Altered rocks, in these contexts, are associated to the ore minerals, but usually represent a waste material. In some cases, however, potassic or sericitic alteration facies may intrinsically constitute the orebody itself. The La Crocetta deposit is a paramount example of how pervasive sericitization of a magmatic rock can result in the formation of high quality raw ceramic material. La Crocetta mine belongs to the Southern Tuscany district that, with its 600.000 tonnes/year, contributes to making Italy the largest European producer of raw ceramic materials.
The material mined at La Crocetta is a porcelaneous whitish rock with high K
2O and low Na
2O, arising from a pervasive hydrothermal alteration of the Capo Bianco porphyritic aplite. A carbonate-rich facies (called "candor"), is present in the south-western part of the mine (
Fig.2). It is associated with the development of abundant carbonate + quartz-pyrite veins, which overprint the pervasive, potassium-rich alteration. These whitish aplitic rocks are named "eurite" and they are characterised by a fine-grained, homogeneous texture with scarce millimetric phenocrysts of quartz, k-feldspar, oligoclase and muscovite. In some localities (e.g. Portoferraio) it contains black-blue aggregates of tourmaline. The eurite can be classified as a subalkaline and peraluminous alkali feldspar granite which was affected by hydrothermal recrystallization of the acidic plagioclase and of the k-feldspar into sericite. The Rb/Sr radiometric study of the magmatic rock indicates an age of about 7.9 Ma, while the hydrothermal alteration occurred about 6.7-6.8 Ma ago.
.jpg)
Fig.2: Simplified geological map of La Crocetta mine. "Candor" alteration facies is indicated by the white shading. CEF = Central Elba Fault; ZF = Zuccale Fault. Modified after Maineri et al., (2003).
Bibliography
• Maineri C., Benvenuti M., Costagliola P., Dini A., Lattanzi P., Ruggieri G. and Villa I.M. (2003) : Sericitic alteration at the La Crocetta deposit (Elba Island, Italy): interplay between magmatism, tectonics and hydrothermal activity. Miner. Deposita, 38, 67-86.
• Benvenuti, M., Costagliola, P., Dini, A., Lattanzi, P., Ruggieri, G., Vaselli, O., & Tanelli, G. (2006). Evolution of the hydrothermal system at La Crocetta feldspar mine: fluid inclusion and stable isotope constraints on the environment of late stage veins. Periodico di Mineralogia, 75(2-3), 39-50.
Foto
.jpg)
Blue tourmaline crystals within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized) and quartz-muscovite vein. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar and quartz-muscovite vein. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz, muscovite (colorless) and k-feldspar (sericitized) and quartz-muscovite vein. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz, muscovite (high interference colors) and k-feldspar. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Blue tourmaline crystals within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Quartz phenocryst within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Quartz phenocryst within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Quartz phenocryst within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Quartz phenocryst within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Feldspar phenocryst (altered) within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Feldspar phenocryst (altered) within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Quartz phenocryst within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Feldspar phenocryst (altered) within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz, muscovite (high interference colors) and k-feldspar. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz, muscovite (high interference colors) and k-feldspar. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz, muscovite (high interference colors) and k-feldspar. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Muscovite phenocryst (colorless) within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Muscovite phenocryst (high interference colors) within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz, muscovite (colorless) and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 2x (Field of view = 7mm) |
.jpg)
Fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz, muscovite (high interference colors) and k-feldspar. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz, muscovite (high interference colors) and k-feldspar. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Feldspar phenocryst (altered) within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz, muscovite and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Feldspar phenocryst (altered) within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz, muscovite (high interference colors) and k-feldspar. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz, muscovite (high interference colors) and k-feldspar. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz, muscovite (high interference colors) and k-feldspar. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Blue tourmaline crystals within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Blue tourmaline crystals within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Blue tourmaline crystals within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Feldspar phenocryst (altered) within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Feldspar phenocryst (altered) within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar (sericitized). Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. PPL image, 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |
.jpg)
Feldspar phenocryst (altered) within fine-grained homogeneous groundmass with millimetric phenocrysts of quartz and k-feldspar. Eurite from la Crocetta mine, Elba Island. XPL image, 10x (Field of view = 2mm) |

.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)